How Can We Help?
In IOTThe Internet of Things (IoT) is the network of physical devices, vehicles, home appliances and other items embedded with electronics, software, sensors, actuators, and connectivity which enables these objects to connect and exchange data. Version 3, Agents – which were formerly known as StreamConsists of a combination of Stream Objects allowing real-time data to flow through. It is created to address a particular use case. Objects in Version 2 – have been distinguished as Virtual and Non-Virtual. At the time of packaging, an Agent Developer will have to specify if an agent is virtual or not. This distinction may never be visible to the end user, however, it is very important to make it as it impacts the behaviour of each agent.
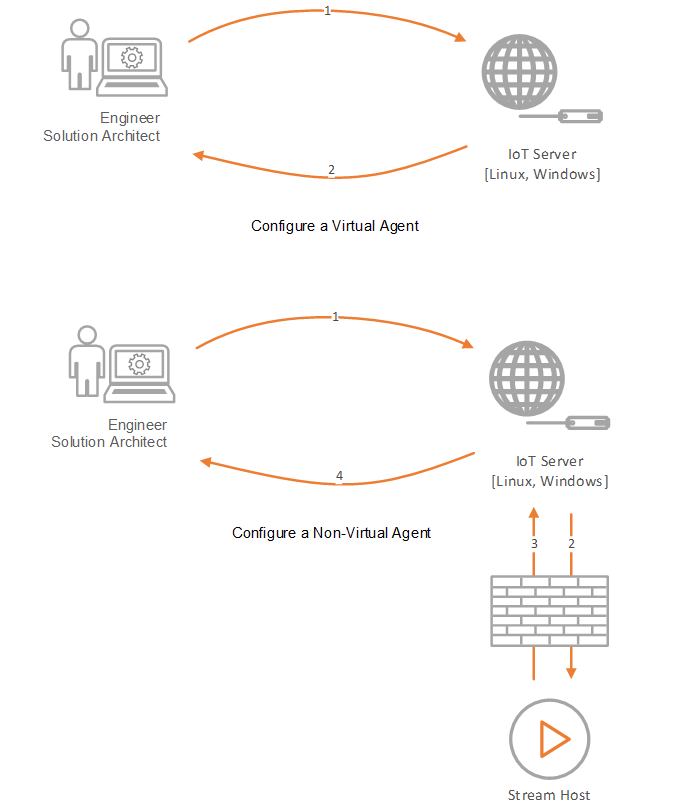
Virtual Agent
A Virtual Agent is one which is not bound to a certain environment in order to functionIs a Stream Objects that performs mathematical and statistical operations., e.g. Azure SQL ListenerIs a Stream Object that is responsible to ingest data from sensors and third party systems. is an agent which can be configured anywhere as it will always have access to the globally available Azure SQL Server which it needs to integrate with.
Non-Virtual Agent
An Agent is Non-Virtual if the system it is to integrate with is only available in a specific environment, e.g. SQL Server Listener is an agent which can only be configured while it is on the same local area network as the intended SQL Server.
As shown in the diagram above, even though both Virtual and Non-Virtual agents ultimately run on the Stream HostIs a client application which hosts/executes the Use Cases designed by the user in the IoT Portal., there is a considerable difference in how they are handled at design time. A Virtual agent can be configured even if no Stream Host is online, but this is not possible for a Non-Virtual one. Virtual agents are also very fast as the engine doesn’t have to go all the way to the Stream Host to configure them and this results into a smoother user experience.

Comments are closed.